Black window opens and closes immediately
Or what are console applications?
Welcome to our website dedicated to console applications. If you've ever encountered a "black window" that opened and immediately closed, and wondered, "What was that?", you're in the right place!
What is it? How to use it?
A program with such a popping-up black window is a console application. It's a program that interacts with the user through a text interface, known as a console or command line. Unlike graphical applications with a nice interface where you can click on buttons and menus, console applications work based on text commands.
First, you need to open the command line (cmd) in Windows. There are at least two ways:
- Through the Start menu: Type cmd or "Command Prompt" in the search and select the appropriate result.
- Using a key combination: Press Win + R, type cmd, and hit Enter.
- New "Terminal" app: You can install the official "Terminal" app from the Microsoft Store. It looks nicer and more convenient than the regular "cmd".
This is what the window looks like:
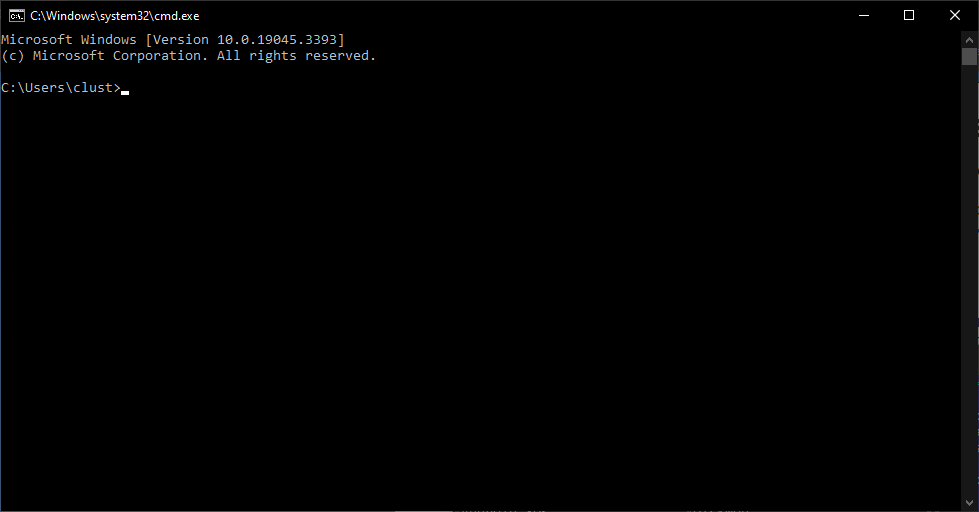
This window is called the command line or console. Here, users input text commands to perform various operations in the system: launch programs, manage files, diagnostics, and much more. Instead of clicking on icons and menus with your mouse, you input specific instructions in text format. It might seem complicated at first glance, but over time you'll master the basic commands and see just how powerful and flexible the console can be.
In the Windows command line, the last line starts with the current directory path followed by the symbol ">". This symbol is called the "command prompt". Commands are input right after this symbol, and the cursor should be blinking there.
Launching a Console Application
To launch a console application, you need to type its name (or the path to it) into the command line and press Enter. For example, to launch an application named "myapp", type:
C:\>myapp
If the application is in a different directory, specify the full path to it:
C:\>D:\Path\to\application\myapp.exe
Using a series of commands, you can easily change the current directory:
C:\>
C:\>d:
D:\>
D:\>cd Path\to\application
D:\Path\to\application>
Passing Parameters
Many console applications accept parameters (or arguments) that allow you to customize their operation. Parameters are specified after the application name:
C:\>myapp parameter1 parameter2
For instance, the ping utility is used to check a server's connection. To test the connection to google.com, type:
C:\ping google.com
Useful Tips:
- Help and Documentation: Most console applications have built-in help that can be accessed using parameters like /help, /?, or -h. Often, it's sufficient to just run the application without parameters.
- Path Auto-completion: In the command line, you can use the Tab key for auto-completion of file names and paths.
- Command History Viewing: Use the up and down arrow keys to view previously entered commands.
- Stopping an Application: If you need to stop an application, press Ctrl + C.
Why make it so complicated!? It's inconvenient.
Console applications and the command line offer several advantages that can make your computer work more efficient and flexible:
- Automation: Console commands allow you to automate routine tasks, such as copying files, cleaning folders, or launching applications at a certain time.
- Creating .bat Files: .bat files allow you to run command sequences automatically. This can be useful for automatic system configurations or performing certain operations regularly.
- Script Writing: With the command line, you can write scripts in various programming languages (e.g., PowerShell, Python, Perl, Bash, or even .bat) that can handle complex tasks without creating a full-fledged application.
- Flexibility and Control: The console provides more granular control of actions and real-time feedback about what's happening in the system.
- Access to Powerful Tools: Many advanced tools and utilities, especially for administration and development, are available exclusively via the command line.
- Cross-platform: Such applications are often developed for Windows, Linux, and Mac simultaneously. Their usage is usually consistent across all platforms.
Files with the .bat extension are executable scripts for Windows, which allow you to automate command sequences in the command line. Such files are especially handy when you need to perform a series of operations regularly or in a particular order, so you don't have to type commands into the console every time. Moreover, .bat files can accept parameters, increasing their flexibility and applicability. Here's an example of such a file:
@echo off
echo Hello, %1!
echo You started this script on %date% at %time%.
pause
In this simple .bat file example, the echo command is used to display text. %1 refers to the first parameter passed to the script. For instance, if you save this script as welcome.bat and run it with the command welcome.bat John, the script will display "Hello, John!". The commands %date% and %time% display the current date and time, respectively.
By familiarizing yourself with creating and working with .bat files, you can automate many tasks, making your computer work even more efficient.
Sometimes, even more complex tasks can be automated. For this, other scripting interpreters can be used. For instance, under Linux, "bash" is often used. Given that the popular video file processing program "ffmpeg" has a console interface, you can automate video processing. For example, I want to process all video files in a directory and keep only the English audio track and English subtitles:
mkdir -p eng
for file in *.mkv
do
audio_stream=0:2
subtitle_stream=$(ffprobe -show_streams -select_streams s -i "$file" 2>&1 | grep subrip | grep -Po \\d:\\d)
echo $audio_stream
echo $subtitle_stream
ffmpeg -i "$file" -map 0:v -map $audio_stream -map $subtitle_stream -c copy "eng/${file}"
done
Of course, such scripts are for advanced users. Don't bother about this for now.
Can it be simpler?
Though the console might seem intimidating at first glance, there are various tools that significantly simplify working with console applications. One such tool is file managers, like the FAR Manager.
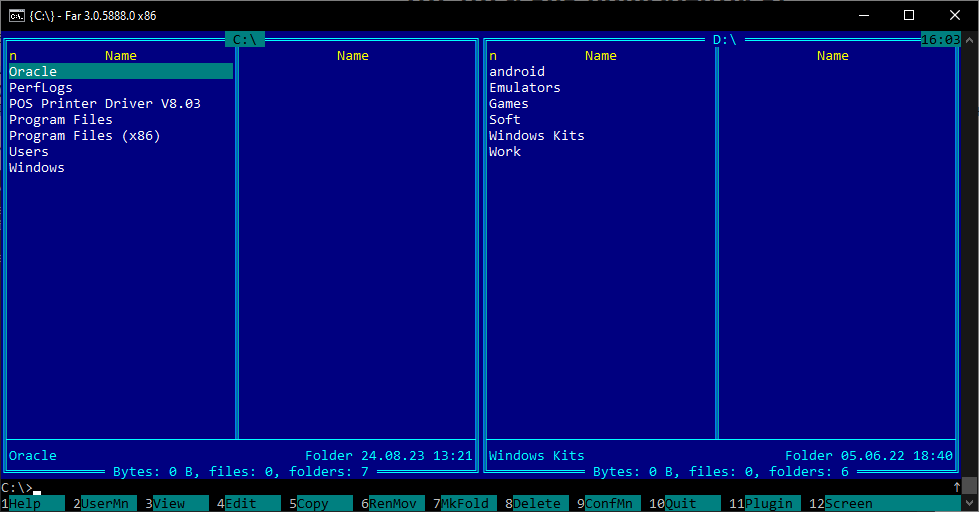
How it makes life easier:
- Quick path copying: In file managers like FAR, you can quickly copy the full path of a file or folder and paste it into the command line, simplifying commands involving that file.
- Command history: FAR and similar managers save a history of entered commands, allowing you to quickly repeat or modify previously entered commands without having to type them again.
- Easy output viewing: With these managers, you can easily view and scroll through the output of a console application, making debugging and analysis processes much simpler.
- Intuitive interface: Many file managers offer a dual-panel interface, simplifying operations like copying and moving files between different directories.
- Plugins and extensions: FAR Manager and other managers often support various plugins, allowing you to extend their functionality and tailor them to your needs.
In conclusion, integrating such tools into your workflow can significantly speed up and ease working with console applications, making it more productive and comfortable.
By mastering the console, you'll unlock a world of new possibilities that make your computer work even simpler and more productive. It might initially seem challenging and inconvenient, but it's all about learning. The console allows you to fully automate a range of routine tasks and also provides tools for fast and accurate problem diagnostics. Besides, many professional tools are available exclusively through the console, making it an indispensable skill for many IT professionals. Over time, having mastered basic commands and techniques, you might begin to prefer the console over the graphical interface due to its efficiency and flexibility.





